Great things in business are never done by one person. They’re done by a team of people. We have that dynamic group of peoples
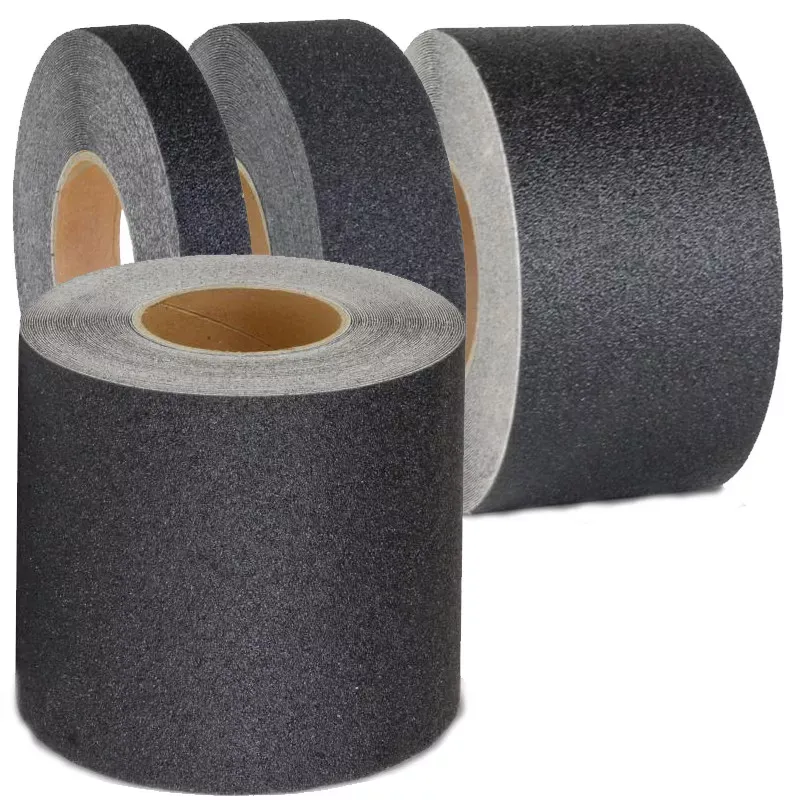

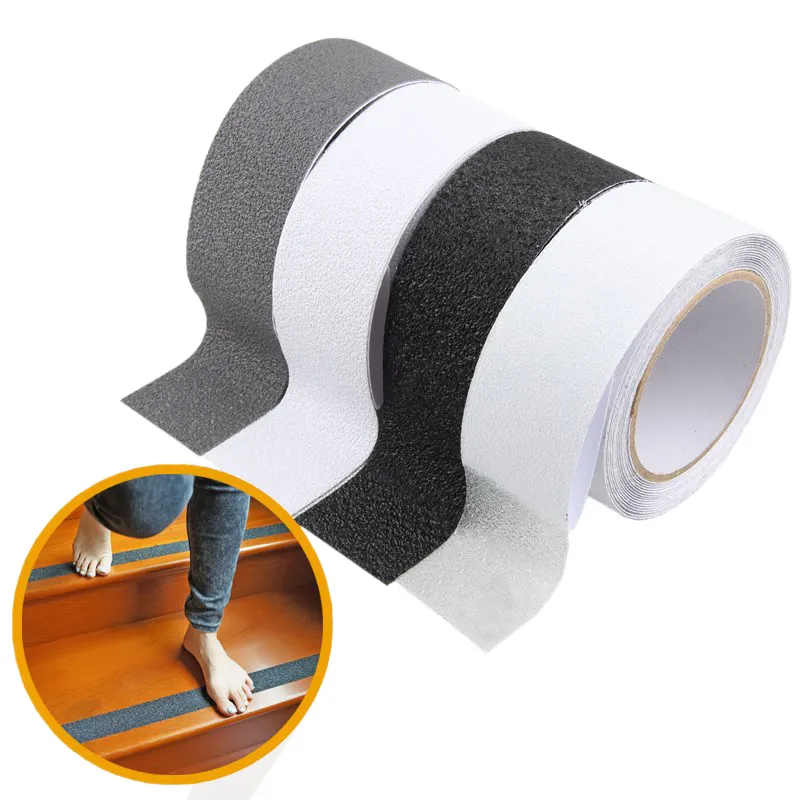
Anti-Slip Tape in Sports Enhancing Performance and Safety
Anti-Slip Tape in Sports: Enhancing Performance and Safety: improving athlete performance, and providing customized support for various disciplines.
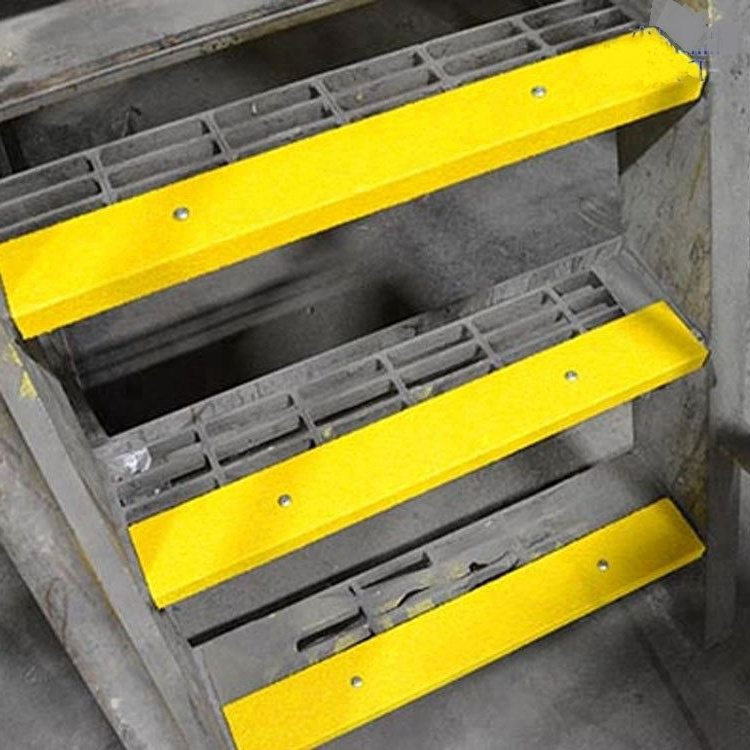

7 Applications of FRP Stair Tread Covers
Explore the versatility and benefits of FRP stair tread covers, highlighting their critical role in enhancing stairway safety and longevity in diverse settings.
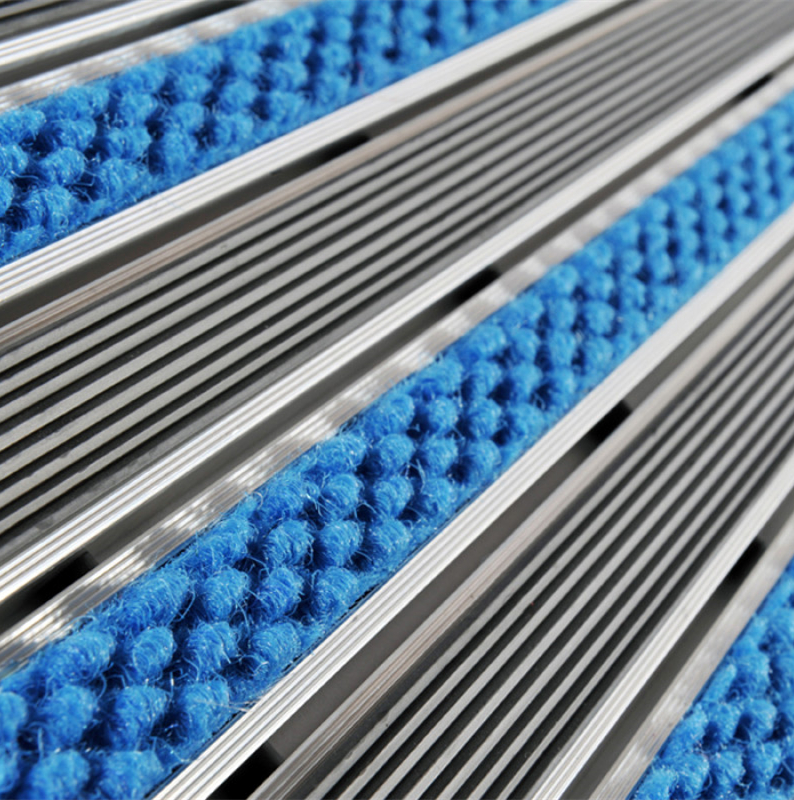
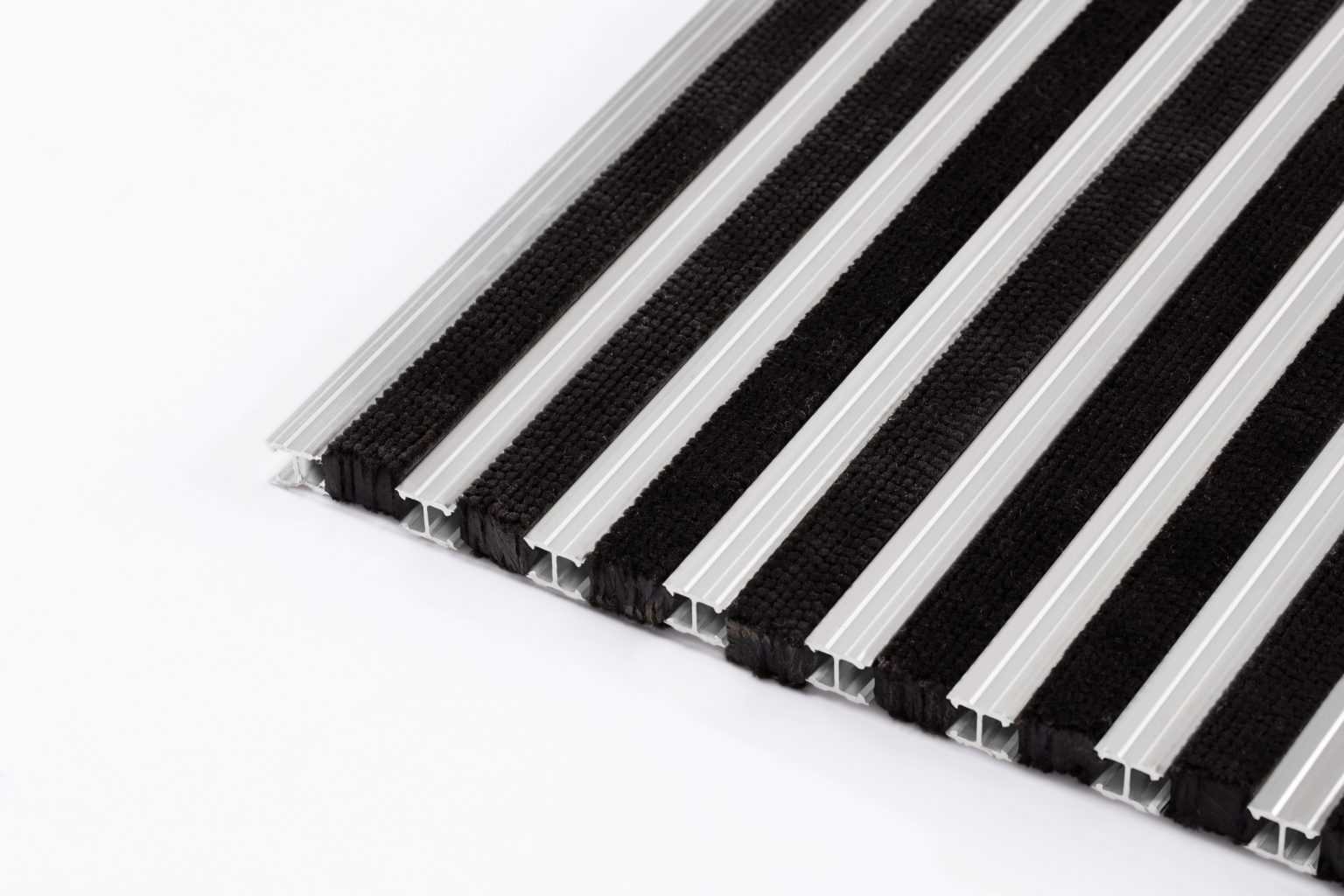
7 Primary Properties of Aluminum Entrance Mattings
Aluminum entrance matting offers seven primary properties that make it highly suitable for use in commercial and high traffic entryways.




